Feb 28 2020
Astronomers Detect Largest Explosion Ever
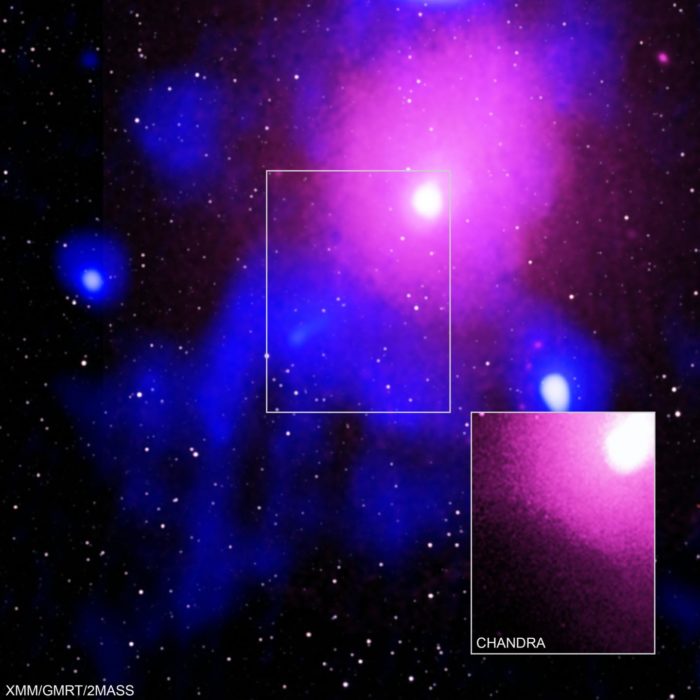 We can quibble about whether or not the Big Bang should be considered an explosion, or whether it happened “in the universe.” It was the expansion of spacetime that is the universe. In any case, astronomers have detected what they think is the biggest explosion (at least discovered so far) since the big bang – in the Ophiuchus galaxy cluster, 390 million light years from us. The explosion is essentially a bubble with a diameter the size of 15 Milky Way galaxies – about 1.5 million light years across. That’s five time bigger than the previous record holder.
We can quibble about whether or not the Big Bang should be considered an explosion, or whether it happened “in the universe.” It was the expansion of spacetime that is the universe. In any case, astronomers have detected what they think is the biggest explosion (at least discovered so far) since the big bang – in the Ophiuchus galaxy cluster, 390 million light years from us. The explosion is essentially a bubble with a diameter the size of 15 Milky Way galaxies – about 1.5 million light years across. That’s five time bigger than the previous record holder.
Astronomers first suspected something was going on when they discovered a big X-ray bubble. They report:
It was discovered in the Chandra X-ray image by Werner and collaborators, who considered a possibility of it being a boundary of an AGN-inflated bubble located outside the core, but discounted this possibility because it required much too powerful an AGN outburst.
An AGN is an active galactic nuclei – more on that below. So they initially discounted it because it was too big, but they then followed up with radio observation, and found an identical radio bubble, confirming that this was a real fossil of an ancient explosion, centered around an AGN. So what’s going on here?
Well, astronomers are not sure. The do not know exactly what may have caused some a massively energetic event. But let’s give some background on AGNs – these are supermassive black holes (SMBH) in the centers of galaxies. Most galaxies have them, including our own. But some supermassive black holes are more super massive than others – getting up to billions of solar masses. More importantly to their activity, some of the black holes are feeding, which means that gas and dust are actively swirling around the event horizon forming an accretion disc and then plunging into the incredible gravity well of the black hole. All that gravity represents an unimaginable amount of energy, and when that gas and dust falls in it swirls around at relativistic speeds – near the speed of light.

 “There is a cult of ignorance in the United States, and there has always been. The strain of anti-intellectualism has been a constant thread winding its way through our political and cultural life, nurtured by the false notion that democracy means that ‘my ignorance is just as good as your knowledge.”
“There is a cult of ignorance in the United States, and there has always been. The strain of anti-intellectualism has been a constant thread winding its way through our political and cultural life, nurtured by the false notion that democracy means that ‘my ignorance is just as good as your knowledge.” The Mars InSight lander is yielding data, and the first slew of papers reporting early results. The two big stories so far is that Mars has more seismic and magnetic activity than previously thought.
The Mars InSight lander is yielding data, and the first slew of papers reporting early results. The two big stories so far is that Mars has more seismic and magnetic activity than previously thought. The use of artificial intelligence in the drug discovery process is not new, but it is advancing in significant ways. Several weeks ago the BBC announced the
The use of artificial intelligence in the drug discovery process is not new, but it is advancing in significant ways. Several weeks ago the BBC announced the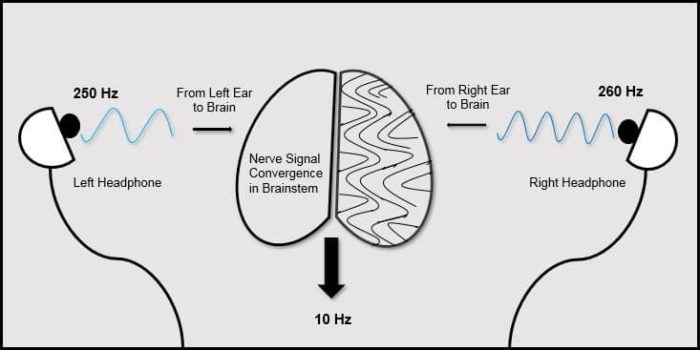 Binaural beats are an auditory illusion created by listening to two tones of slightly different frequency. This produces a type of feedback effect in the brain that produces a third illusory sound that has a pulsating quality, hence binaural beats. All perceptual illusions are fascinating, at least to neuroscientists, because they are clues to how the brain processes sensory information. What we ultimately perceive is the result of a complex constructive process (not passive recording) and understanding the process offers insight into the strengths and weaknesses of human perception.
Binaural beats are an auditory illusion created by listening to two tones of slightly different frequency. This produces a type of feedback effect in the brain that produces a third illusory sound that has a pulsating quality, hence binaural beats. All perceptual illusions are fascinating, at least to neuroscientists, because they are clues to how the brain processes sensory information. What we ultimately perceive is the result of a complex constructive process (not passive recording) and understanding the process offers insight into the strengths and weaknesses of human perception. One of the frustrating things I encounter as a practicing physician is listening to patients describe how they are motivated to improve their health, and then list all the things they are doing, none of which will improve their health. I am eating organic, taking probiotics, taking supplements, and “eating clean.” They may go into detail about their “paleo” diet, some specific megavitamin or superfood, or list the herbal supplements they think will supercharge some aspect of their health.
One of the frustrating things I encounter as a practicing physician is listening to patients describe how they are motivated to improve their health, and then list all the things they are doing, none of which will improve their health. I am eating organic, taking probiotics, taking supplements, and “eating clean.” They may go into detail about their “paleo” diet, some specific megavitamin or superfood, or list the herbal supplements they think will supercharge some aspect of their health. Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon, is the
Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon, is the  This weekend I was at the AAAS (American Association for the Advancement of Science) meeting in Seattle talking about science communication. The meeting often creates a pulse of science-news reporting, base on all the presentations and lectures there. One talk I didn’t get to see was
This weekend I was at the AAAS (American Association for the Advancement of Science) meeting in Seattle talking about science communication. The meeting often creates a pulse of science-news reporting, base on all the presentations and lectures there. One talk I didn’t get to see was  Migraines are a complex neurological phenomenon that offer a window into some general principles of brain function.
Migraines are a complex neurological phenomenon that offer a window into some general principles of brain function.  Homeopathy
Homeopathy 




