Apr
26
2024
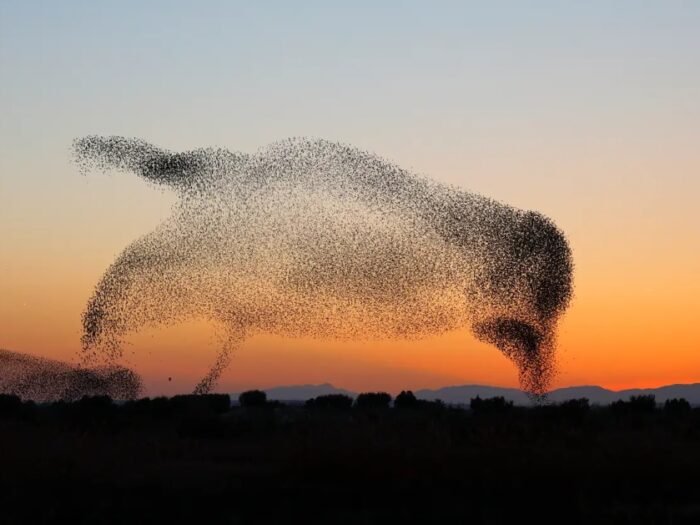 Most people have watched large flocks of birds. They are fascinating, and have interested scientists for a long time. How, exactly, do so many birds maintain their cohesion as a flock? It’s obviously a dynamic process, but what are the mechanisms?
Most people have watched large flocks of birds. They are fascinating, and have interested scientists for a long time. How, exactly, do so many birds maintain their cohesion as a flock? It’s obviously a dynamic process, but what are the mechanisms?
When I was young I was taught that each flock had a leader, and the other birds were ultimately just following that leader. When two smaller flocks combined into a larger flock, then one of those leaders become dominant and takes over the combined flock. But this explanation is largely untrue. It actually depends a great deal on the species of bird and the type of flock.
The “follow the leader” method is essentially what is happening with the V formations. These are obviously very different from the murmurations of small birds morphing like a giant flying amoeba. Some species, like pigeons, use a combined strategy, still following a leader, but more of a hierarchy of leaders, which can change over time.
For the more dynamic flocks, like starlings, researchers found that there is no leader or hierarchy. Every bird is just following the flock itself. It is a great example of an emergent phenomenon in nature. It’s like ants working in a colony or a bee hive – each individual bee or ant does not really know what the entire colony is doing, and there is no leader or foreman calling the shots or directing traffic. Each individual is just following a simple algorithm, and the collective complexity emerges from that.
Continue Reading »
Mar
04
2024
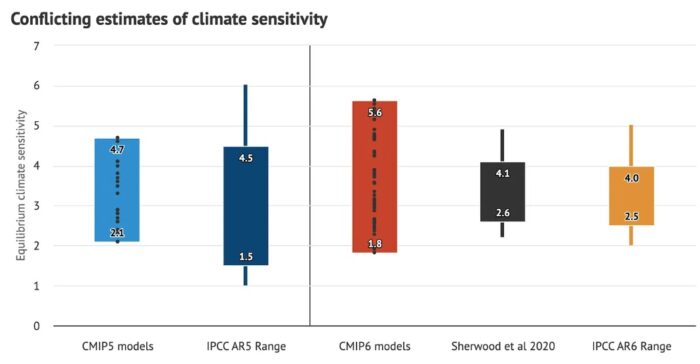 I love to follow kerfuffles between different experts and deep thinkers. It’s great for revealing the subtleties of logic, science, and evidence. Recently there has been an interesting online exchange between a physicists science communicator (Sabine Hossenfelder) and some climate scientists (Zeke Hausfather and Andrew Dessler). The dispute is over equilibrium climate sensitivity (ECS) and the recent “hot model problem”.
I love to follow kerfuffles between different experts and deep thinkers. It’s great for revealing the subtleties of logic, science, and evidence. Recently there has been an interesting online exchange between a physicists science communicator (Sabine Hossenfelder) and some climate scientists (Zeke Hausfather and Andrew Dessler). The dispute is over equilibrium climate sensitivity (ECS) and the recent “hot model problem”.
First let me review the relevant background. ECS is a measure of how much climate warming will occur as CO2 concentration in the atmosphere increases, specifically the temperature rise in degrees Celsius with a doubling of CO2 (from pre-industrial levels). This number of of keen significance to the climate change problem, as it essentially tells us how much and how fast the climate will warm as we continue to pump CO2 into the atmosphere. There are other variables as well, such as other greenhouse gases and multiple feedback mechanisms, making climate models very complex, but the ECS is certainly a very important variable in these models.
There are multiple lines of evidence for deriving ECS, such as modeling the climate with all variables and seeing what the ECS would have to be in order for the model to match reality – the actual warming we have been experiencing. Therefore our estimate of ECS depends heavily on how good our climate models are. Climate scientists use a statistical method to determine the likely range of climate sensitivity. They take all the studies estimating ECS, creating a range of results, and then determine the 90% confidence range – it is 90% likely, given all the results, that ECS is between 2-5 C.
Continue Reading »
Jan
08
2024
 Categorization is critical in science, but it is also very tricky, often deceptively so. We need to categorize things to help us organize our knowledge, to understand how things work and relate to each other, and to communicate efficiently and precisely. But categorization can also be a hindrance – if we get it wrong, it can bias or constrain our thinking. The problem is that nature rarely cleaves in straight clean lines. Nature is messy and complicated, almost as if it is trying to defy our arrogant attempts at labeling it. Let’s talk a bit about how we categorize things, how it can go wrong, and why it matters.
Categorization is critical in science, but it is also very tricky, often deceptively so. We need to categorize things to help us organize our knowledge, to understand how things work and relate to each other, and to communicate efficiently and precisely. But categorization can also be a hindrance – if we get it wrong, it can bias or constrain our thinking. The problem is that nature rarely cleaves in straight clean lines. Nature is messy and complicated, almost as if it is trying to defy our arrogant attempts at labeling it. Let’s talk a bit about how we categorize things, how it can go wrong, and why it matters.
We can start with an example that might seem like a simple category – what is a planet? Of course, any science nerd knows how contentious the definition of a planet can be, which is why it is a good example. Astronomers first defined them as wandering stars – the points of light that were not fixed but seemed to wonder throughout the sky. There was something different about them. This is often how categories begin – we observe a phenomenon we cannot explain and so the phenomenon is the category. This is very common in medicine. We observe a set of signs and symptoms that seem to cluster together, and we give it a label. But once we had a more evolved idea about the structure of the universe, and we knew that there are stars and stars have lots of stuff orbiting around them, we needed a clean way to divide all that stuff into different categories. One of those categories is “planet”. But how do we define planet in an objective, intuitive, and scientifically useful way?
This is where the concept of “defining characteristic” comes in. A defining characteristic is, “A property held by all members of a class of object that is so distinctive that it is sufficient to determine membership in that class. A property that defines that which possesses it.” But not all categories have a clear defining characteristic, and for many categories a single characteristic will never suffice. Scientists can and do argue about which characteristics to include as defining, which are more important, and how to police the boundaries of that characteristic.
Continue Reading »
Jan
02
2024
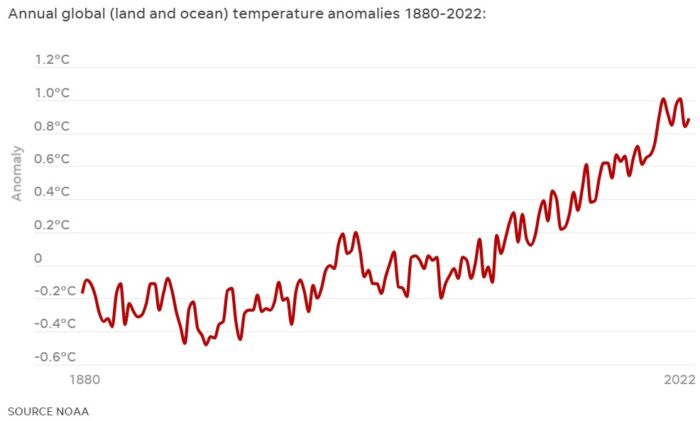 What everyone knew was coming is now official – 2023 was the warmest year on record. This means we can also say that the last 10 years are the hottest decade on record. 2023 dethrones 2016 as the previous warmest year and bumps 2010 out of the top 10. Further, in the last half of the year, many of the months were the hottest months on record, and by a large margin. September’s average temperature was 1.44 C above pre-industrial levels, beating the previous record set in 2020 of 0.98 C. The average for 2023 is 1.4 C, beating the previous record in 2016 of 1.2 C. This also makes 2023 probably the warmest year in the last 125,000 years.
What everyone knew was coming is now official – 2023 was the warmest year on record. This means we can also say that the last 10 years are the hottest decade on record. 2023 dethrones 2016 as the previous warmest year and bumps 2010 out of the top 10. Further, in the last half of the year, many of the months were the hottest months on record, and by a large margin. September’s average temperature was 1.44 C above pre-industrial levels, beating the previous record set in 2020 of 0.98 C. The average for 2023 is 1.4 C, beating the previous record in 2016 of 1.2 C. This also makes 2023 probably the warmest year in the last 125,000 years.
There is no mystery as to why this is happening, and it’s exactly what scientists predicted would happen. Remember the global warming “pause” that was allegedly happening between 1998 and 2012? This was the pause that never was, a short term fluctuation in the long term trend and a bit of statistical voodoo. Global warming deniers were declaring that global warming was over, it was never real, it was just a statistical fluke and the world was regressing back to the mean. Meanwhile, scientists said the long term trend had not altered and predicted the next decade would be even warmer. In retrospect, it turns out that during the alleged “pause” more heat was going into the oceans and was not fully reflected in surface temperatures.
The best test of a scientific hypothesis is its ability to make predictions about future data. The deniers were predicting that the Earth would simply return to baseline temperatures, while the scientific community were united in predicting that the next decade (now the past decade) would see continued warming.
Continue Reading »
Dec
05
2023
 One of the greatest mysteries of modern science is how to unite the two overarching theories of physics – quantum mechanics and general relativity. If physicists could somehow unite these two theories, which currently do not play well together, then we might get to a deeper “one theory to rule them all.”
One of the greatest mysteries of modern science is how to unite the two overarching theories of physics – quantum mechanics and general relativity. If physicists could somehow unite these two theories, which currently do not play well together, then we might get to a deeper “one theory to rule them all.”
Quantum mechanics essentially says that we do not live in a classical universe. Classical physics as it operates on the macroscopic scale is just the surface level, the end result of a quantum universe at the near atomic and smaller scale. At the quantum scale (not to be confused with the Quantum Realm fantasy of Marvel – don’t get me started), reality is quantized and probabilistic. Things that seem like magic on the macro scale are reality at the quantum scale, like wave particle duality and entanglement.
General relativity, rather, deals with the super big scale, spacetime itself. Einstein postulated that gravity is the result of spacetime being curved. Freely moving objects actually always travel in a straight line, but through curved space. Mass curves space, which is how mass creates gravity. This is, as least, a reasonable lay person’s understanding of these concepts.
Continue Reading »
Oct
10
2023
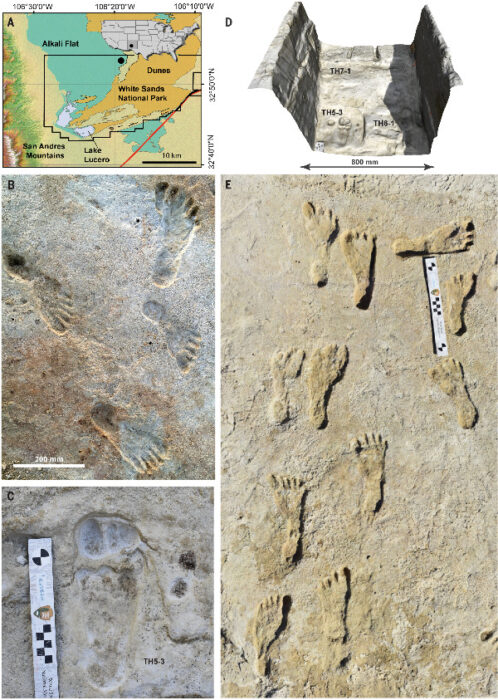 Exactly when Homo sapiens came to the Americas has not been firmly established, and new evidence has just thrown another curve ball into the controversy.
Exactly when Homo sapiens came to the Americas has not been firmly established, and new evidence has just thrown another curve ball into the controversy.
There is evidence of a large culture of humans throughout North America from 12-13,000 years ago, called the Clovis Culture. The Clovis people are known almost entirely from the stone points they left behind, which have a characteristic shape – a lance-shaped tip with fluting at the base. The flutes likely made it easier to attach the points to a shaft. Archaeologists have collected over 10,000 Clovis points across North America, indicating the culture was extensive. However, we only have a single human skeleton associated with Clovis points – the burial site of a 1 – 1.5 year old boy found at the Anzick Site, in Wilsall, Montana. This did allow for DNA analysis showing the the Clovis people were likely direct ancestors of later Native Americans.
Evidence of pre-Clovis people in the Americas has been controversial, but over the years enough evidence has emerged to doom the “Clovis first” hypothesis in favor of the existence of pre-Clovis people. The latest evidence came from the Cooper’s Ferry site in Idaho, which appears to be a human habitation site with hearths and animal bones, carbon dated to 16,500 years ago. But there are still skeptics who say it is not absolutely clear that the site was the result of human habitation. Sometimes carbon dating is called into question – was there mixing of material, for example. The Clovis and pre-Clovis evidence also tends to contain either artifacts or bones, but rarely both together, which makes it difficult to nail down the timing.
Continue Reading »
Oct
03
2023
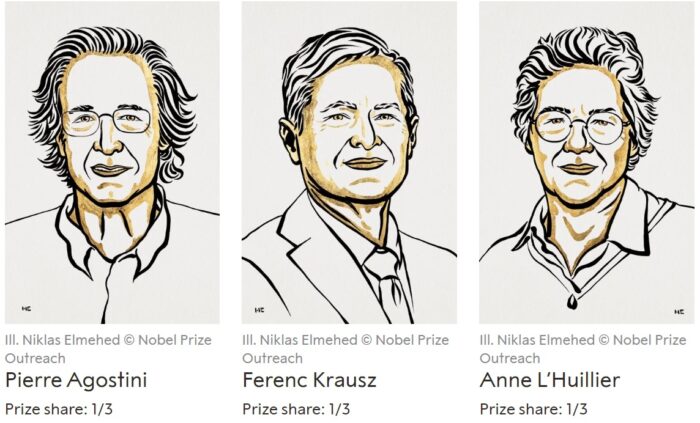 One attosecond (as) is 1×10−18 seconds. An attosecond is to one second what one second is to the age of the universe. It is an extremely tiny slice of time. This year’s Nobel Prize in physics goes to three scientists, Pierre Agostini, Ferenc Krausz, and Anne L’Huillier, whose work contributed to developing pulses of light that are measured in attoseconds.
One attosecond (as) is 1×10−18 seconds. An attosecond is to one second what one second is to the age of the universe. It is an extremely tiny slice of time. This year’s Nobel Prize in physics goes to three scientists, Pierre Agostini, Ferenc Krausz, and Anne L’Huillier, whose work contributed to developing pulses of light that are measured in attoseconds.
Why are such short pulses of light useful? Because they allow for experiments that capture the physical state of processes that happen extremely fast. In particular, they are the first light pulses fast enough to capture information about the state of electrons in atoms, molecules, and condensed matter.
Anne L’Huillier, only the fifth woman to win the Nobel Prize in Physics, discovered in 1987 that when she shined infrared light through a noble gas it would give off overtones, which are other frequencies of light. The light would give extra energy to atoms in the gas, some of which would then radiate that energy away as additional photons of light. This was foundational work that made possible the later discoveries by Agostini and Krausz. Essentially these overtones were harmonic frequencies of light, multiples of the original light frequency.
L’Huillier and her colleagues later published in 1991 follow up work explaining a plateau observed in the harmonic pulses of light. They found that the high-harmonic generation (HHG) plateau was a single electron phenomenon. At the time they proposed that, in theory, it might be possible to exploit this phenomenon to generate very short pulses of light.
In 2001 both Krausz and Ferenc, in separate experiments, were able to build on this work to produce attosecond scale pulses of light. Krausz was able to generate pulses of 650 attoseconds, and Ferenc of 250 attoseconds. Here are some technical details:
Continue Reading »
Sep
28
2023
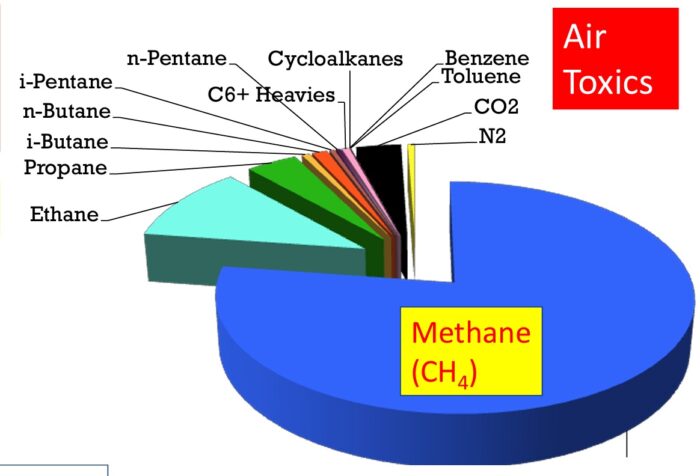 In the last 18 years, since 2005, the US has decreased our CO2 emissions due to electricity generation by 32%, 819 million metric tons of CO2 per year. Thirty percent of this decline can be attributed to renewable energy generation. But 65% is attributed to essentially replacing coal-fired plants with natural gas (NG) fired plants. The share of coal decreased from 50% to 23% while the share of NG increased from 19% to 38%. Burning coal for energy released about twice as much CO2 as burning NG. Plus, NG power plants are more efficient than coal. The net result is that NG releases about 30% of the CO2 per unit of energy created as does coal.
In the last 18 years, since 2005, the US has decreased our CO2 emissions due to electricity generation by 32%, 819 million metric tons of CO2 per year. Thirty percent of this decline can be attributed to renewable energy generation. But 65% is attributed to essentially replacing coal-fired plants with natural gas (NG) fired plants. The share of coal decreased from 50% to 23% while the share of NG increased from 19% to 38%. Burning coal for energy released about twice as much CO2 as burning NG. Plus, NG power plants are more efficient than coal. The net result is that NG releases about 30% of the CO2 per unit of energy created as does coal.
But – the picture is more complicated than just calculating CO2 release. The implications of a true comparison between these two sources of energy has huge implications for our attempts at reducing climate change. It’s clear that we should phase out all fossil fuels as quickly as possible. But this transition is going to take decades and cost trillions. Meanwhile, we are already skirting close to the line in terms of peak warming and the consequences of that warming. We no longer have the luxury of just developing low carbon technology with the knowledge that it will ultimately replace fossil fuels. The path we take to get to net zero matters. We need to take the path that lowers greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions as quickly as possible. So when we build more wind, solar, nuclear, hydroelectric, and geothermal plants, do we shut down coal, natural gas, or perhaps it doesn’t matter?
If we look just at CO2, it’s a no-brainer – coal is much worse and we should prioritize shutting down coal-fired plants. This may still be the ultimate answer, but there is another factor to consider. NG contains methane, and methane is also a GHG. Per molecule, methane causes 80 times the warming of CO2 over a 20 year period. So any true comparison between coal and NG must also consider methane. (A little methane is also released in coal mining.) But considering methane is extremely complicated, and involves choices when looking at the data that don’t have any clear right or wrong answers.
Continue Reading »
Jul
07
2023
 Are attitudes towards genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in our agriculture softening? Back in 2015 a Pew survey found that the gap between public opinion and that of scientists was greatest on acceptance of GMOs (more than any other topic surveyed), with a 51% gap. But more recent data shows declining opposition. Regulators are also softening their stance, with Mexico walking back a ban on GMO corn from the US, and the EU considering softer rules on GMOs. Some countries, like the US, have also adopted new terminology, such as bioengineered, and carved out separate rules for crops made with altered genes but not with transgene insertions.
Are attitudes towards genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in our agriculture softening? Back in 2015 a Pew survey found that the gap between public opinion and that of scientists was greatest on acceptance of GMOs (more than any other topic surveyed), with a 51% gap. But more recent data shows declining opposition. Regulators are also softening their stance, with Mexico walking back a ban on GMO corn from the US, and the EU considering softer rules on GMOs. Some countries, like the US, have also adopted new terminology, such as bioengineered, and carved out separate rules for crops made with altered genes but not with transgene insertions.
We still have a way to go, and there is still enough opposition to slow adoption of useful agricultural technology. I like to think this is because the science is slowly winning the day. I do think many environmentalists have their heart in the right place, but sometimes get distracted by ideological positions, such as an aversion to anything “unnatural” or high tech. But if the stakes get high enough, the more moderate environmentalists can change their position. I think we are seeing this with nuclear power and the need to combat global warming. And I think we are seeing this with GMOs and the need to feed the world without destroying the environment. The benefits of GMOs are ultimately just too great to ignore.
But there is a lot of inertia in the anti-GMO propaganda that Greenpeace, the organic lobby, and others have been spreading for two decades. I was just recently asked about one specific claim that reflects the nature of this propaganda and how sticky it can be – aren’t GMOs killing the butterflies? The short answer is no, but as always the full story has lots of details. Here is a typical headline from the Environmental Working Group (who I personally find to be more ideological than science-based) – GMO-Linked Herbicide May Doom Monarch Butterflies. This framing was lazily reproduced by most mainstream reporting, but it is nothing but anti-GMO propaganda.
Continue Reading »
Mar
31
2023
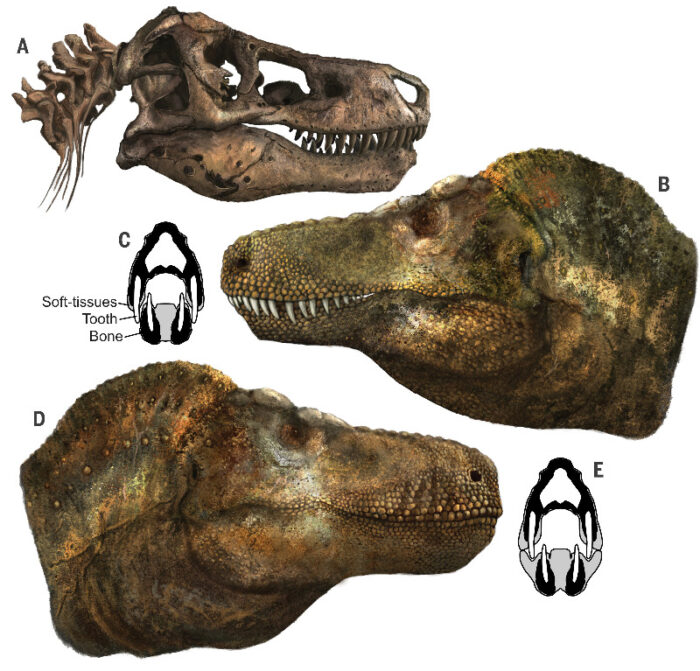 One of the challenges of paleontology is that we are trying to infer and entire animal just from the hard parts that fossilize, mostly bones and teeth (and sometimes just teeth). But if we look at animals today there are a lot of details we could not guess from their bones alone – the mane of a lion, the humps on camels, or the amazing display of peacocks. Soft tissue is rarely preserved, so in many cases we simply have to guess. If we look at the classic depictions of dinosaurs, we see creatures that are all drab in color and don’t have any significant soft-tissue adaptations. We are getting better and inferring color from fossilized melanosomes. We are also discovering that many dinosaurs had feathers, and those feathers were probably colorful. In fact, that clade (just think of birds) have lots of integumentary adaptations, not just feathers. Turkeys are a good example. It’s just as likely, therefore, that dinosaurs had lots of interesting integumentary structures hanging off of them.
One of the challenges of paleontology is that we are trying to infer and entire animal just from the hard parts that fossilize, mostly bones and teeth (and sometimes just teeth). But if we look at animals today there are a lot of details we could not guess from their bones alone – the mane of a lion, the humps on camels, or the amazing display of peacocks. Soft tissue is rarely preserved, so in many cases we simply have to guess. If we look at the classic depictions of dinosaurs, we see creatures that are all drab in color and don’t have any significant soft-tissue adaptations. We are getting better and inferring color from fossilized melanosomes. We are also discovering that many dinosaurs had feathers, and those feathers were probably colorful. In fact, that clade (just think of birds) have lots of integumentary adaptations, not just feathers. Turkeys are a good example. It’s just as likely, therefore, that dinosaurs had lots of interesting integumentary structures hanging off of them.
A recent study highlights one method that scientists can use to gain more information about the soft tissue of dinosaurs. They looked at the teeth of T. rex, crocodilians, and lizards. Their question was – did T. rex have a toothy smile like an alligator, or fleshy lips covering their teeth like lizards? They have been imagined both ways, but Jurassic Park probably solidified the image for many people of a toothy T. rex. There is definitely something more menacing about a grill of visible deadly carnivore teeth.
What they did was look at the teeth, which is the hardest part of vertebrates and fossilize very well. Specifically they looked at the wear on the teeth. If fleshy lips covered the teeth, they would have been protected from wear along the covered surface. When looking at the teeth of crocodilians vs lizards we see this difference. So all we have to do is examine T-rex teeth to see if they have wear patterns that look like a crocodiles or a lizards. They also did an analysis of skull size and tooth length to see if there was also a relationship there. They found:
Contrary to depictions that have dominated for more than a century, they found that theropods, including T. rex, had lips that covered their teeth, leaving them looking more like modern Komodo dragons than crocodiles.
Continue Reading »
 Most people have watched large flocks of birds. They are fascinating, and have interested scientists for a long time. How, exactly, do so many birds maintain their cohesion as a flock? It’s obviously a dynamic process, but what are the mechanisms?
Most people have watched large flocks of birds. They are fascinating, and have interested scientists for a long time. How, exactly, do so many birds maintain their cohesion as a flock? It’s obviously a dynamic process, but what are the mechanisms?
 I love to follow kerfuffles between different experts and deep thinkers. It’s great for revealing the subtleties of logic, science, and evidence. Recently there has been an interesting online exchange between a physicists science communicator (
I love to follow kerfuffles between different experts and deep thinkers. It’s great for revealing the subtleties of logic, science, and evidence. Recently there has been an interesting online exchange between a physicists science communicator ( Categorization is critical in science, but it is also very tricky, often deceptively so. We need to categorize things to help us organize our knowledge, to understand how things work and relate to each other, and to communicate efficiently and precisely. But categorization can also be a hindrance – if we get it wrong, it can bias or constrain our thinking. The problem is that nature rarely cleaves in straight clean lines. Nature is messy and complicated, almost as if it is trying to defy our arrogant attempts at labeling it. Let’s talk a bit about how we categorize things, how it can go wrong, and why it matters.
Categorization is critical in science, but it is also very tricky, often deceptively so. We need to categorize things to help us organize our knowledge, to understand how things work and relate to each other, and to communicate efficiently and precisely. But categorization can also be a hindrance – if we get it wrong, it can bias or constrain our thinking. The problem is that nature rarely cleaves in straight clean lines. Nature is messy and complicated, almost as if it is trying to defy our arrogant attempts at labeling it. Let’s talk a bit about how we categorize things, how it can go wrong, and why it matters. What everyone knew was coming is now official – 2023 was the warmest year on record. This means we can also say that the last 10 years are the
What everyone knew was coming is now official – 2023 was the warmest year on record. This means we can also say that the last 10 years are the  One of the greatest mysteries of modern science is how to unite the two overarching theories of physics – quantum mechanics and general relativity. If physicists could somehow unite these two theories, which currently do not play well together, then we might get to a deeper “one theory to rule them all.”
One of the greatest mysteries of modern science is how to unite the two overarching theories of physics – quantum mechanics and general relativity. If physicists could somehow unite these two theories, which currently do not play well together, then we might get to a deeper “one theory to rule them all.” Exactly when Homo sapiens came to the Americas has not been firmly established, and new evidence has just thrown another curve ball into the controversy.
Exactly when Homo sapiens came to the Americas has not been firmly established, and new evidence has just thrown another curve ball into the controversy. One attosecond (as) is 1×10−18 seconds. An attosecond is to one second what one second is to the age of the universe. It is an extremely tiny slice of time.
One attosecond (as) is 1×10−18 seconds. An attosecond is to one second what one second is to the age of the universe. It is an extremely tiny slice of time.  In the last 18 years, since 2005, the US has
In the last 18 years, since 2005, the US has  Are attitudes towards genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in our agriculture softening? Back in 2015
Are attitudes towards genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in our agriculture softening? Back in 2015  One of the challenges of paleontology is that we are trying to infer and entire animal just from the hard parts that fossilize, mostly bones and teeth (and sometimes just teeth). But if we look at animals today there are a lot of details we could not guess from their bones alone – the mane of a lion, the humps on camels, or the amazing display of peacocks. Soft tissue is rarely preserved, so in many cases we simply have to guess. If we look at the classic depictions of dinosaurs, we see creatures that are all drab in color and don’t have any significant soft-tissue adaptations. We are getting better and inferring color from fossilized melanosomes. We are also discovering that many dinosaurs had feathers, and those feathers were probably colorful. In fact, that clade (just think of birds) have lots of integumentary adaptations, not just feathers. Turkeys are a good example. It’s just as likely, therefore, that dinosaurs had lots of interesting integumentary structures hanging off of them.
One of the challenges of paleontology is that we are trying to infer and entire animal just from the hard parts that fossilize, mostly bones and teeth (and sometimes just teeth). But if we look at animals today there are a lot of details we could not guess from their bones alone – the mane of a lion, the humps on camels, or the amazing display of peacocks. Soft tissue is rarely preserved, so in many cases we simply have to guess. If we look at the classic depictions of dinosaurs, we see creatures that are all drab in color and don’t have any significant soft-tissue adaptations. We are getting better and inferring color from fossilized melanosomes. We are also discovering that many dinosaurs had feathers, and those feathers were probably colorful. In fact, that clade (just think of birds) have lots of integumentary adaptations, not just feathers. Turkeys are a good example. It’s just as likely, therefore, that dinosaurs had lots of interesting integumentary structures hanging off of them.




